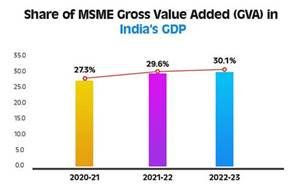
The MSME sector continues to be a cornerstone of India’s economic growth, contributing significantly to employment, manufacturing, and exports. In recent years, the sector has displayed remarkable resilience, with its share in the country’s Gross Value Added (GVA) increasing from 27.3% in 2020-21 to 29.6% in 2021-22 and 30.1% in 2022-23, highlighting its growing role in national economic output.
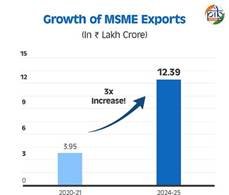
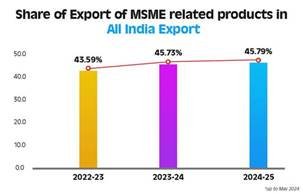
Exports from MSMEs have seen substantial growth, rising from ₹3.95 lakh crore in 2020-21 to ₹12.39 lakh crore in 2024-25. The number of exporting MSMEs has also surged, increasing from 52,849 in 2020-21 to 1,73,350 in 2024-25. Their contribution to India’s total exports has steadily grown, reaching 43.59% in 2022-23, 45.73% in 2023-24, and 45.79% in 2024-25 (up to May 2024). These trends underscore the sector’s increasing integration into global trade and its potential to drive India’s position as a manufacturing and export hub.
Source: https://pib.gov.in/
In the Union Budgdet 2024-25 presented on July 23, 2024, Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman introduced several measures aimed at bolstering India’s Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs). These initiatives are designed to enhance credit access, provide technological support, and facilitate market expansion for MSMEs. Below are the key announcements:
- Credit Guarantee Scheme for Manufacturing MSMEs: A new scheme will facilitate term loans for MSMEs to purchase machinery and equipment without requiring collateral or third-party guarantees. A self-financing guarantee fund will offer guarantee covers up to ₹100 crore per applicant, with borrowers responsible for upfront and annual guarantee fees.
- Enhanced Credit Assessment Models: Public sector banks are set to develop in-house capabilities for MSME credit assessment, moving away from reliance on external evaluations. This new model will utilize MSMEs’ digital footprints, providing a more comprehensive view of their creditworthiness beyond traditional asset or turnover metrics.
- Support During Financial Stress: A mechanism has been introduced to ensure the continuation of bank credit to MSMEs during periods of financial stress. While in the ‘Special Mention Account’ stage, MSMEs will receive credit support backed by a government-promoted fund, helping them avoid transitioning into non-performing assets.
- Increased MUDRA Loan Limits: The maximum limit for MUDRA loans under the ‘Tarun’ category has been doubled from ₹10 lakh to ₹20 lakh. This enhancement benefits entrepreneurs who have previously availed and successfully repaid such loans, providing them with greater financial support for business expansion.
- Expansion of TReDS Platform: To improve MSMEs’ working capital management, the turnover threshold for mandatory onboarding of buyers onto the Trade Receivables Discounting System (TReDS) platform has been reduced from ₹500 crore to ₹250 crore. This measure is expected to bring an additional 22 Central Public Sector Enterprises (CPSEs) and 7,000 companies onto the platform, facilitating quicker realization of receivables for MSMEs.
- SIDBI Branch Expansion: The Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI) will open 24 new branches within the year, aiming to serve all major MSME clusters within three years. This expansion will increase service coverage to 168 out of 242 major clusters, providing MSMEs with improved access to direct credit and support services.
- Support for Food Processing MSMEs: Financial assistance will be provided for establishing 50 multi-product food irradiation units within the MSME sector. Additionally, the setup of 100 food quality and safety testing laboratories with NABL accreditation will be facilitated, enhancing product quality and compliance with international standards.
- E-Commerce Export Hubs: To enable MSMEs and traditional artisans to access international markets, e-commerce export hubs will be established in a public-private partnership (PPP) mode. These hubs will offer a seamless regulatory framework, consolidating trade facilitation services under one roof.
These strategic initiatives reflect the government’s commitment to strengthening the MSME sector, recognizing its pivotal role in employment generation, entrepreneurship, and economic growth.
Sources: